View on QuantumAI View on QuantumAI
|
 Run in Google Colab Run in Google Colab
|
 View source on GitHub View source on GitHub
|
|
try:
import cirq
except ImportError:
print("installing cirq...")
!pip install --quiet cirq
print("installed cirq.")
This notebook demonstrates how to use the functionality in cirq.experiments to run Isolated XEB end-to-end. "Isolated" means we do one pair of qubits at a time.
import cirq
import numpy as np
Set up Random Circuits
We create a library of 20 random, two-qubit circuits using the sqrt(ISWAP) gate on the two qubits we've chosen.
from cirq.experiments import random_quantum_circuit_generation as rqcg
circuits = rqcg.generate_library_of_2q_circuits(
n_library_circuits=20,
two_qubit_gate=cirq.ISWAP**0.5,
q0=cirq.GridQubit(4, 4),
q1=cirq.GridQubit(4, 5),
)
print(len(circuits))
20
# We will truncate to these lengths
max_depth = 100
cycle_depths = np.arange(3, max_depth, 20)
cycle_depths
array([ 3, 23, 43, 63, 83])
Set up a Sampler.
For demonstration, we'll use a density matrix simulator to sample noisy samples. However, input a device_name (and have an authenticated Google Cloud project name set as your GOOGLE_CLOUD_PROJECT environment variable) to run on a real device.
device_name = None # change me!
if device_name is None:
sampler = cirq.DensityMatrixSimulator(noise=cirq.depolarize(5e-3))
else:
import cirq_google as cg
sampler = cg.get_engine_sampler(device_name, gate_set_name='sqrt_iswap')
device = cg.get_engine_device(device_name)
import cirq.contrib.routing as ccr
graph = ccr.gridqubits_to_graph_device(device.qubits)
pos = {q: (q.row, q.col) for q in graph.nodes}
import networkx as nx
nx.draw_networkx(graph, pos=pos)
Take Data
from cirq.experiments.xeb_sampling import sample_2q_xeb_circuits
sampled_df = sample_2q_xeb_circuits(
sampler=sampler, circuits=circuits, cycle_depths=cycle_depths, repetitions=10_000
)
sampled_df
100%|██████████| 108/108 [00:18<00:00, 5.93it/s]
Benchmark fidelities
from cirq.experiments.xeb_fitting import benchmark_2q_xeb_fidelities
fids = benchmark_2q_xeb_fidelities(
sampled_df=sampled_df, circuits=circuits, cycle_depths=cycle_depths
)
fids
%matplotlib inline
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
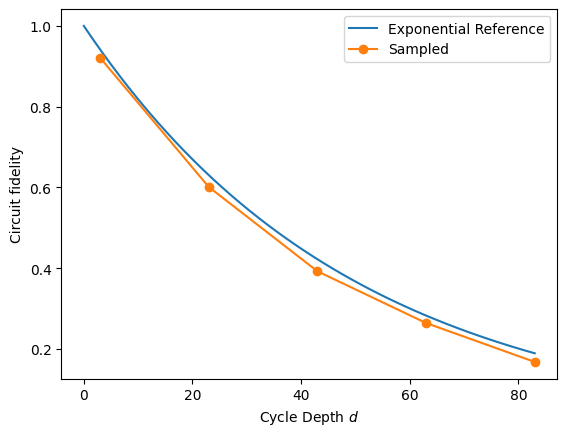
# Exponential reference
xx = np.linspace(0, fids['cycle_depth'].max())
plt.plot(xx, (1 - 5e-3) ** (4 * xx), label=r'Exponential Reference')
def _p(fids):
plt.plot(fids['cycle_depth'], fids['fidelity'], 'o-', label=fids.name)
fids.name = 'Sampled'
_p(fids)
plt.ylabel('Circuit fidelity')
plt.xlabel('Cycle Depth $d$')
plt.legend(loc='best')
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0x7f4a4e57d2a0>
Optimize PhasedFSimGate parameters
We know what circuits we requested, and in this simulated example, we know what coherent error has happened. But in a real experiment, there is likely unknown coherent error that you would like to characterize. Therefore, we make the five angles in PhasedFSimGate free parameters and use a classical optimizer to find which set of parameters best describes the data we collected from the noisy simulator (or device, if this was a real experiment).
import multiprocessing
pool = multiprocessing.get_context('spawn').Pool()
from cirq.experiments.xeb_fitting import (
parameterize_circuit,
characterize_phased_fsim_parameters_with_xeb,
SqrtISwapXEBOptions,
)
# Set which angles we want to characterize (all)
options = SqrtISwapXEBOptions(
characterize_theta=True,
characterize_zeta=True,
characterize_chi=True,
characterize_gamma=True,
characterize_phi=True,
)
# Parameterize the sqrt(iswap)s in our circuit library
pcircuits = [parameterize_circuit(circuit, options) for circuit in circuits]
# Run the characterization loop
characterization_result = characterize_phased_fsim_parameters_with_xeb(
sampled_df,
pcircuits,
cycle_depths,
options,
pool=pool,
# ease tolerance so it converges faster:
fatol=5e-3,
xatol=5e-3,
)
Simulating with theta = -0.785 zeta = 0 chi = 0 gamma = 0 phi = 0 Loss: 0.531 Simulating with theta = -0.685 zeta = 0 chi = 0 gamma = 0 phi = 0 Loss: 0.581 Simulating with theta = -0.785 zeta = 0.1 chi = 0 gamma = 0 phi = 0 Loss: 0.564 Simulating with theta = -0.785 zeta = 0 chi = 0.1 gamma = 0 phi = 0 Loss: 0.553 Simulating with theta = -0.785 zeta = 0 chi = 0 gamma = 0.1 phi = 0 Loss: 0.595 Simulating with theta = -0.785 zeta = 0 chi = 0 gamma = 0 phi = 0.1 Loss: 0.564 Simulating with theta = -0.745 zeta = 0.04 chi = 0.04 gamma = -0.1 phi = 0.04 Loss: 0.61 Simulating with theta = -0.775 zeta = 0.01 chi = 0.01 gamma = 0.05 phi = 0.01 Loss: 0.554 Simulating with theta = -0.881 zeta = 0.044 chi = 0.044 gamma = 0.02 phi = 0.044 Loss: 0.601 Simulating with theta = -0.734 zeta = 0.011 chi = 0.011 gamma = 0.005 phi = 0.011 Loss: 0.543 Simulating with theta = -0.761 zeta = 0.0484 chi = 0.0484 gamma = 0.022 phi = -0.0916 Loss: 0.572 Simulating with theta = -0.779 zeta = 0.0121 chi = 0.0121 gamma = 0.0055 phi = 0.0521 Loss: 0.544 Simulating with theta = -0.759 zeta = -0.0868 chi = 0.0532 gamma = 0.0242 phi = 0.0292 Loss: 0.578 Simulating with theta = -0.779 zeta = 0.0533 chi = 0.0133 gamma = 0.00605 phi = 0.00731 Loss: 0.539 Simulating with theta = -0.77 zeta = 0.0206 chi = 0.0446 gamma = -0.0434 phi = 0.0182 Loss: 0.551 Simulating with theta = -0.754 zeta = 0.0388 chi = -0.0676 gamma = -0.0107 phi = 0.0354 Loss: 0.564 Simulating with theta = -0.777 zeta = 0.0097 chi = 0.0581 gamma = -0.00268 phi = 0.00886 Loss: 0.535 Simulating with theta = -0.772 zeta = 0.0139 chi = -0.00676 gamma = 0.0489 phi = 0.0135 Loss: 0.559 Simulating with theta = -0.77 zeta = 0.0189 chi = 0.0317 gamma = -0.0203 phi = 0.017 Loss: 0.534 Simulating with theta = -0.759 zeta = 0.0251 chi = 0.0336 gamma = -0.0103 phi = -0.0344 Loss: 0.55 Simulating with theta = -0.774 zeta = 0.0153 chi = 0.0175 gamma = 0.00156 phi = 0.0305 Loss: 0.534 Simulating with theta = -0.82 zeta = 0.0279 chi = 0.0372 gamma = -0.0112 phi = 0.0145 Loss: 0.548 Simulating with theta = -0.756 zeta = 0.0152 chi = 0.0176 gamma = 0.000962 phi = 0.0119 Loss: 0.533 Simulating with theta = -0.767 zeta = -0.0296 chi = 0.0366 gamma = -0.0142 phi = 0.02 Loss: 0.536 Simulating with theta = -0.77 zeta = -0.00891 chi = 0.0308 gamma = -0.00917 phi = 0.0168 Loss: 0.531 Simulating with theta = -0.765 zeta = 0.00652 chi = -0.0191 gamma = -0.0081 phi = 0.0216 Loss: 0.537 Simulating with theta = -0.774 zeta = 0.0089 chi = 0.0388 gamma = -0.00404 phi = 0.012 Loss: 0.531 Simulating with theta = -0.773 zeta = -0.00667 chi = 0.0101 gamma = 0.016 phi = 0.0115 Loss: 0.533 Simulating with theta = -0.769 zeta = -0.0119 chi = 0.0215 gamma = -4.04e-05 phi = -0.0096 Loss: 0.529 Simulating with theta = -0.767 zeta = -0.0256 chi = 0.0234 gamma = -0.000839 phi = -0.0296 Loss: 0.533 Simulating with theta = -0.768 zeta = 0.00799 chi = 0.0333 gamma = -0.0209 phi = 0.000983 Loss: 0.536 Simulating with theta = -0.772 zeta = -0.003 chi = 0.0159 gamma = 0.00679 phi = 0.00884 Loss: 0.53 Simulating with theta = -0.792 zeta = -0.0212 chi = 0.0252 gamma = -0.00354 phi = -0.000627 Loss: 0.533 Simulating with theta = -0.765 zeta = 0.00612 chi = 0.0195 gamma = -0.000165 phi = 0.00874 Loss: 0.53 Simulating with theta = -0.777 zeta = 0.00895 chi = 0.00746 gamma = 0.0102 phi = -0.00879 Loss: 0.529 Simulating with theta = -0.78 zeta = 0.0179 chi = -0.00421 gamma = 0.0199 phi = -0.0216 Loss: 0.531 Simulating with theta = -0.757 zeta = 0.00362 chi = 0.0412 gamma = 0.00509 phi = 0.0045 Loss: 0.532 Simulating with theta = -0.778 zeta = 0.000905 chi = 0.0103 gamma = 0.00127 phi = 0.00112 Loss: 0.529 Simulating with theta = -0.77 zeta = -0.00848 chi = -0.00896 gamma = 0.0113 phi = -0.0119 Loss: 0.533 Simulating with theta = -0.773 zeta = 0.00456 chi = 0.0269 gamma = -0.000214 phi = 0.00605 Loss: 0.529 Simulating with theta = -0.773 zeta = 0.00645 chi = 0.0183 gamma = -0.00237 phi = -0.00983 Loss: 0.529 Simulating with theta = -0.783 zeta = -0.00254 chi = 0.0143 gamma = 0.0037 phi = -0.0172 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.792 zeta = -0.00688 chi = 0.0117 gamma = 0.00563 phi = -0.0301 Loss: 0.53 Simulating with theta = -0.785 zeta = 0.0192 chi = 0.00944 gamma = 0.00507 phi = -0.00184 Loss: 0.53 Simulating with theta = -0.773 zeta = -0.00413 chi = 0.0184 gamma = 0.00124 phi = -0.00766 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.773 zeta = 0.00441 chi = 0.0238 gamma = 0.00374 phi = -0.0161 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.771 zeta = 0.00616 chi = 0.0306 gamma = 0.00497 phi = -0.0247 Loss: 0.529 Simulating with theta = -0.779 zeta = -0.00195 chi = 0.018 gamma = 0.00983 phi = -0.00762 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.782 zeta = -0.00615 chi = 0.0179 gamma = 0.0159 phi = -0.00652 Loss: 0.529 Simulating with theta = -0.781 zeta = -0.00266 chi = 0.00596 gamma = 0.0117 phi = -0.029 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.779 zeta = -0.0117 chi = 0.0248 gamma = 0.00189 phi = -0.0222 Loss: 0.529 Simulating with theta = -0.778 zeta = -0.00654 chi = 0.0204 gamma = 0.00396 phi = -0.0189 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.785 zeta = 0.000411 chi = 0.0146 gamma = 0.0119 phi = -0.0278 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.791 zeta = 0.00268 chi = 0.0126 gamma = 0.0173 phi = -0.0379 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.779 zeta = 0.000178 chi = 0.0305 gamma = 0.00158 phi = -0.00603 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.774 zeta = 0.00115 chi = 0.0287 gamma = 0.00872 phi = -0.0134 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.777 zeta = -0.00119 chi = 0.0117 gamma = 0.0137 phi = -0.0275 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.784 zeta = -0.00766 chi = 0.0136 gamma = 0.0155 phi = -0.022 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.781 zeta = 0.00284 chi = 0.0142 gamma = 0.0199 phi = -0.0205 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.782 zeta = 0.000175 chi = 0.015 gamma = 0.0181 phi = -0.0368 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.783 zeta = 0.00124 chi = 0.0135 gamma = 0.0222 phi = -0.0515 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.776 zeta = 0.00901 chi = 0.0201 gamma = 0.0134 phi = -0.0284 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.782 zeta = 0.00662 chi = 0.0253 gamma = 0.0151 phi = -0.0233 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.784 zeta = 0.0105 chi = 0.0321 gamma = 0.0158 phi = -0.0212 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.786 zeta = -0.00453 chi = 0.019 gamma = 0.0161 phi = -0.0203 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.782 zeta = -0.00131 chi = 0.0269 gamma = 0.00807 phi = -0.0282 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.782 zeta = 0.0018 chi = 0.0174 gamma = 0.017 phi = -0.0224 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.792 zeta = 0.000646 chi = 0.00784 gamma = 0.0226 phi = -0.0389 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.779 zeta = 0.00102 chi = 0.0235 gamma = 0.0122 phi = -0.0198 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.779 zeta = 0.00163 chi = 0.0255 gamma = 0.0194 phi = -0.0212 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.777 zeta = 0.00223 chi = 0.031 gamma = 0.0232 phi = -0.018 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.775 zeta = 0.00903 chi = 0.0237 gamma = 0.0166 phi = -0.0291 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.778 zeta = 0.00564 chi = 0.0225 gamma = 0.0165 phi = -0.0269 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.778 zeta = 0.00651 chi = 0.0306 gamma = 0.014 phi = -0.00861 Loss: 0.528 Simulating with theta = -0.781 zeta = 0.00176 chi = 0.0189 gamma = 0.0171 phi = -0.0298 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.778 zeta = 0.00486 chi = 0.0289 gamma = 0.0152 phi = -0.026 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.78 zeta = 0.00718 chi = 0.025 gamma = 0.0211 phi = -0.0311 Loss: 0.526 Simulating with theta = -0.781 zeta = 0.0103 chi = 0.0258 gamma = 0.0256 phi = -0.0368 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.777 zeta = 0.00181 chi = 0.023 gamma = 0.0206 phi = -0.0307 Loss: 0.526 Simulating with theta = -0.774 zeta = -0.000604 chi = 0.0219 gamma = 0.0233 phi = -0.0344 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.78 zeta = 0.00234 chi = 0.0171 gamma = 0.0227 phi = -0.0299 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.781 zeta = 0.000245 chi = 0.0213 gamma = 0.0239 phi = -0.0302 Loss: 0.526 Simulating with theta = -0.783 zeta = -0.00245 chi = 0.0207 gamma = 0.0276 phi = -0.0318 Loss: 0.526 Simulating with theta = -0.78 zeta = 0.00371 chi = 0.0166 gamma = 0.0227 phi = -0.0395 Loss: 0.527 Simulating with theta = -0.78 zeta = 0.00215 chi = 0.0233 gamma = 0.0203 phi = -0.0258 Loss: 0.526 Simulating with theta = -0.779 zeta = 0.00291 chi = 0.0276 gamma = 0.0185 phi = -0.0291 Loss: 0.526 Simulating with theta = -0.778 zeta = 0.00396 chi = 0.0292 gamma = 0.0247 phi = -0.029 Loss: 0.526 Simulating with theta = -0.779 zeta = 0.00341 chi = 0.0266 gamma = 0.0228 phi = -0.0292 Loss: 0.526 Simulating with theta = -0.778 zeta = -0.00298 chi = 0.0237 gamma = 0.0212 phi = -0.0269 Loss: 0.526 Simulating with theta = -0.778 zeta = -0.000436 chi = 0.024 gamma = 0.0212 phi = -0.028 Loss: 0.526
characterization_result.final_params
{(cirq.GridQubit(4, 4),
cirq.GridQubit(4, 5)): {'theta': np.float64(-0.7783379736657015), 'zeta': np.float64(-0.00043573822845567947), 'chi': np.float64(0.0240391542895369), 'gamma': np.float64(0.021218997340166138), 'phi': np.float64(-0.027952516833367733)} }
characterization_result.fidelities_df
from cirq.experiments.xeb_fitting import before_and_after_characterization
before_after_df = before_and_after_characterization(fids, characterization_result)
before_after_df
from cirq.experiments.xeb_fitting import exponential_decay
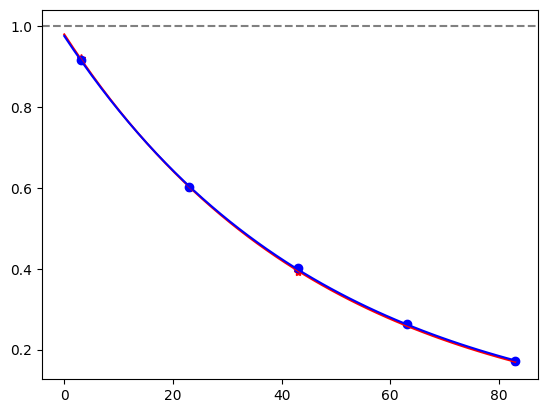
for i, row in before_after_df.iterrows():
plt.axhline(1, color='grey', ls='--')
plt.plot(row['cycle_depths_0'], row['fidelities_0'], '*', color='red')
plt.plot(row['cycle_depths_c'], row['fidelities_c'], 'o', color='blue')
xx = np.linspace(0, np.max(row['cycle_depths_0']))
plt.plot(xx, exponential_decay(xx, a=row['a_0'], layer_fid=row['layer_fid_0']), color='red')
plt.plot(xx, exponential_decay(xx, a=row['a_c'], layer_fid=row['layer_fid_c']), color='blue')
plt.show()